What is a stress echocardiogram?
 A stress echocardiogram is a study that combines echocardiograms and standard stress testing. An echocardiogram is a test that uses high-pitched sound waves (ultrasound) to produce an image of the heart. The sound waves are sent through a device called a transducer. The sound waves travel through the chest and bounce off the heart creating echoes which are captured by the transducer. These echoes are converted into moving pictures of the heart that can be seen on a video monitor.
A stress echocardiogram is a study that combines echocardiograms and standard stress testing. An echocardiogram is a test that uses high-pitched sound waves (ultrasound) to produce an image of the heart. The sound waves are sent through a device called a transducer. The sound waves travel through the chest and bounce off the heart creating echoes which are captured by the transducer. These echoes are converted into moving pictures of the heart that can be seen on a video monitor.
There is no radiation involved with ultrasound and it has no negative effect on biological tissue. A stress echo involves an echocardiogram of the heart at rest and a second echocardiogram after the heart has been exercised (or stressed) either by walking on a treadmill or by injection of a drug that speeds up the heart without exercise.
What information does a stress echocardiogram provide about the heart?
An echocardiogram is generally used to evaluate heart wall thickness and motion, as well as the structure and function of the heart valves. An echocardiogram can also be used to estimate the amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each heartbeat (ejection fraction).
The stress test portion of the stress echo is used to look for areas of the heart that may have blockages which can only be detected when the heart is exercising. The test can identify areas of poor blood flow in the heart, areas of heart muscle that are not contracting normally, previous injury to the heart muscle caused by impaired blood flow, or evidence of heart failure, especially in people with chest pain or a possible heart attack.
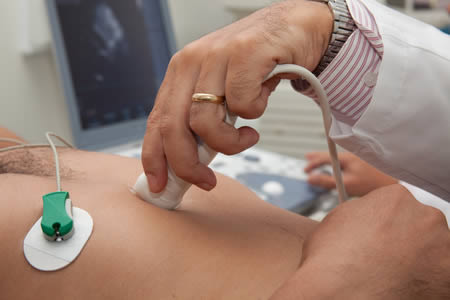
How is the test performed?
You will be asked to wear a gown with clothes removed from the waist up and to lie on your back on an exam table. Sticky patches or electrodes are attached to the chest and shoulders and connected to electrodes or wires to record the electrocardiogram (EKG). The technician will apply a clear gel to your chest which helps transmit the sound waves.
During the exam you may be asked to hold your breath or take deep breaths. You may also hear a “whooshing” sound which is the sound of the blood flowing through the heart.
Following the “resting” echocardiogram, the stress test portion of the study will be performed. You will be asked to walk on a treadmill to exercise the heart. Your blood pressure and EKG will be monitored as you walk on the treadmill. The speed and incline of the treadmill will be increased every 3 minutes just like a standard exercise test which will increase you heart rate. If you are not able to walk on a treadmill, you will be given an intravenous drug called Dobutamine, which makes the heart beat faster – as if you were exercising.
After the stress test portion of the exam, the echocardiogram will be repeated as described above. The entire stress echocardiogram test takes approximately 1 hour. You will be able to leave after the test is completed.
How do I prepare for the test?
Do not eat or drink for three hours prior to the procedure. Diabetics, particularly those who use insulin, will need special instructions from the physician’s office. Your physician may instruct you to stop specific heart medicines one or two days prior to the test. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes that are suitable for exercise.



